Outrageous Predictions
Carry trade unwind brings USD/JPY to 100 and Japan’s next asset bubble
Charu Chanana
Chief Investment Strategist
Steen Jakobsen
Chief Investment Officer
Summary: Weakening the Killer Dollar will likely put the final nail in the coffin of the grand credit cycle.
When history is written, 2019 will most likely be remembered as the beginning of the end of the biggest monetary experiment ever — the year that kicked off a global recession despite the lowest ever nominal and real interest rates in history. Monetary policy has reached the end of a very long road and has proven a failure. This is the legacy of Milton Friedman and others, who probably never expected a world in which central banks would consider and even enact negative yields to the extent we see today.
There are many reasons why monetary policy does not work over the full cycle, but first among them is the fact that classic easy-money monetary policy only works in “normal times”. Once rates get too high or low, the standard rules and models break down.
Take an emerging-market country like Argentina, for example, which should see massive inflow of capital with its 80% policy rate. Capital, meanwhile, should be fleeing Germany and its deeply negative yields. Instead, money is fleeing Argentina and being hoarded in Germany.
In our quarterly outlook at Saxo Bank, rather than looking for an extension of current conditions, we try to look ahead at the next likely policy response, given those conditions. In Q3 we — too early it turns out — suggested that fiscal stimulus was on the way after hitting the nail on the head in Q1 and Q2 with The Policy Panic (Fed hard reverse!) and False Stabilisation themes respectively. Our outlook for Q4 is the Killer Dollar. In a global system of failed monetary policies and a long and difficult path to fiscal policy, there is only one other tool left in the box for the global economy and that is lower the price of global money itself: the US dollar.
There is an estimated USD 240 trillion of debt in the world, roughly 240% of global GDP. Far too much of this debt is denominated in US dollars due to the dollar’s role as reserve currency and the deep liquidity of the US capital markets.
In this respect, the prospects for all asset classes become a function of US dollar liquidity and direction. If the dollar rises too much, the strain in the system increases: not only for US export, but also for the emerging market with its high dependence on USD funding and export machines.
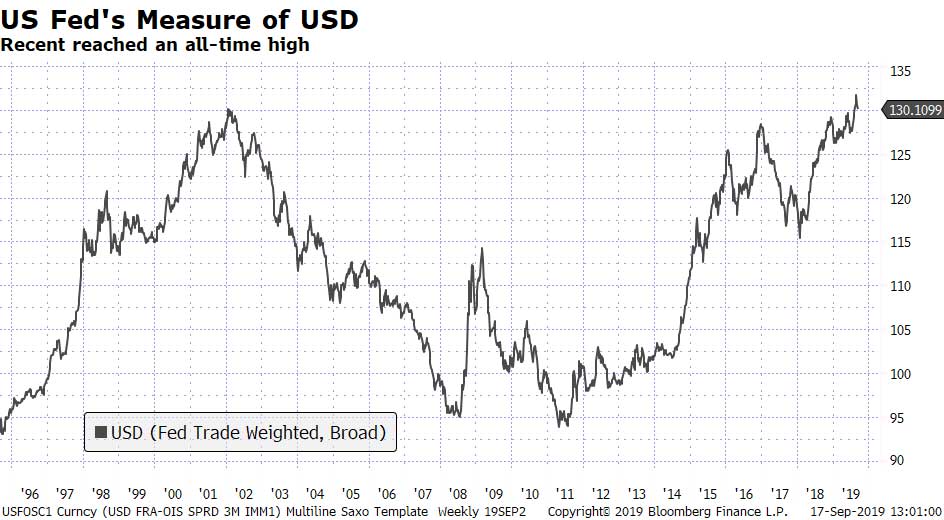
The Fed’s measure of the USD is at its strongest ever – north of even the 2002 peak and currently above 130 — versus a level of around 100 as recently as 2013.
US dollar liquidity, meanwhile, is going from scarce to scarcer, as our Christopher Dembik points out in his piece in this outlook, contracting even after the Fed has moved into an easing cycle.
A stronger US dollar and tight USD liquidity will weigh on global growth and create de facto disinflation despite central banks efforts to lower policy rates. Those low rates and the myopic focus on inflation targeting are adding to the damage by driving an egregious misallocation of capital that destroys productivity. The credit mechanism and productive allocation of capital are by far the most important factors for long-term growth.
Into this mix comes President Trump with his calls for a weaker USD. His first avenue for this is the clumsy attempt to bully the Fed to cut interest rates. When – and not if – his patience with the Powell Fed runs out, he is likely to activate the 1934 Gold Reserve Act which gives the White House broad powers to intervene by selling dollars to buy foreign currency. The Treasury keeps a fund of USD 95 billion for this purpose. Furthermore, the Fed could print ‘new dollarsʼ and warehouse some of the intervention, so there is no real upper limit to the amount of intervention possible. Since 1995 the US has intervened only three times: 1998, 2000 and 2011, every time for international liquidity provision purposes.
Another important angle here is that USD intervention has bipartisan support — Elisabeth Warren is among the voices in Congress calling for a weaker dollar. In her new Economic Patriotism plan she talks about managing the dollar via taxing capital inflow.
The same mechanism is found in the bipartisan Baldwin-Hadley bill. That bill would give power to Fed to tax US capital inflows to weaken the dollar. This reflects President Trump’s successful campaign to make the trade deficit an issue and an enemy of the US. It also ties in well with US- China trade talks, which few people think will help reduce the value of the dollar.
In short, US policymakers of all stripes are increasingly warming to active policies intended to reduce USD strength, an extension of Trump’s move away from multilateral global institutions and “America First” stance. It’s a true case of an us versus them mentality.
Remember that all of this is happening at a time where the global credit impulse is weak and getting weaker, where credit transmission is structurally difficult and setting up a lack of support for the real economy and finally, where the oil of the machine, the USD, is strong and in short supply.
That’s not to say that the gambit to weaken the USD will succeed. The going it alone, beggar-thy-neighbour policy will not Make America Great Again, it will do the opposite: Create a fragmented system supported by government and central banks but without proper market forces and access to distribute money and credit.
Weakening the Killer Dollar will likely put the final nail in the coffin of the grand credit cycle that started in the early 1980s, when the US balance sheet was reset and the USD was anchored by Volcker’s victory over inflation after Nixon abandoned the gold standard in 1971. The grand cycle since then has been turbocharged by globalisation and by lending money into existence via offshore USD creation (EuroDollars). A weaker USD can only buy us some time, it won’t offer a structural solution. It’s the easiest quick fix to what ails global markets, and the one with the least political resistance. The mighty dollar is set to tumble. But be careful what you wish for, USA.