Quarterly Outlook
Q3 Investor Outlook: Beyond American shores – why diversification is your strongest ally
Jacob Falkencrone
Global Head of Investment Strategy
Head of Macroeconomic Research
Summary: The beta version of our brand new CDS monitor allows you to track the latest developments and anomalies in the sovereign CDS market that may impact your investment strategies. The below chart bar shows you the evolution of 5-year CDS for the main developed and emerging economies.
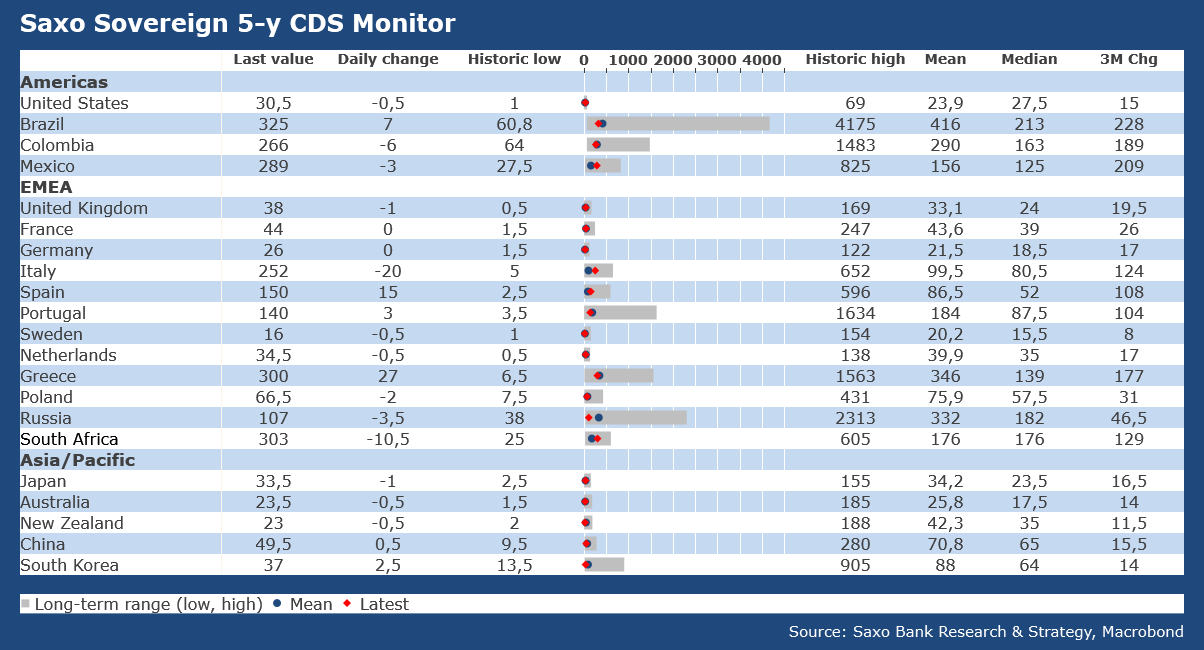
In this note today, I will focus on two countries that are in the spotlight: Italy and South Africa.
Ahead of the crucial EUCO meeting that will take place tonight and of Italy's credit rating review by S&P on Friday, sentiment towards Italian risk has increased with the 5-year CDS spread trading at 252bp. It is back to the level reached at the time of the budget confrontation with the EU in Autumn 2018. However, it is still much lower than during the European sovereign debt crisis when it climbed to more than 600bp before the ECB steps in in the market to stem panic.
Lower confidence is also reflected by higher pessimism among investors about Italexit. As usual, private investors are more pessimistic than institutional investors. The risk of break-up measured by Sentix as the probability the country leaves the eurozone within one year has jumped from 5% in February to 14% in March. The one-month surge is impressive, but the measure of the risk is still lower than in Spring 2018 when Italy was facing for the umpteenth time a political drama.
Overall, tensions remain contained, and the likelihood that CDS spread increases above the 300bp threshold is extremely limited due to decisive action of the ECB. The central bank is literally cleaning up all the secondary market, with a total amount of asset purchases that will surpass the 2016 record at ϵ1.1tr this year. In addition, yesterday's ECB monetary policy tweak to accept some junk-rated debt as collateral for its loans to banks serves as a perfect shield to protect Italy against upcoming rating cuts. I would bet my bonus for the year 2020 that a euro debt crisis will not happen in 2020 or in 2021.
On another note, South Africa’s 5-year CDS has receded from its peak of mid-March, but it is still elevated at 313bp, which is way above its long-term average of 175bp. Markets have reacted very positively to the SARB’s aggressive monetary policy tweak and subdued inflation opens the door to further rate cuts in May (likely by 50bp to 3.75%). That being said, the central bank cannot address the significant country’s external financing needs and the only way to reassure investors is to negotiate external support. South Africa’s president Ramaphosa has confirmed earlier this week that he is in talks with the IMF and other multilateral organizations to have access to rapid financing instrument resources. The activation of the IMF’s Rapid Financing Instrument (RFI), with little strings attached, could be announced in the coming days, which would ease tensions in the CDS market.