AI bubble: How big, how long, and what could break it
Charu Chanana
Chief Investment Strategist
Key points:
- AI valuations keep stretching, but earnings growth and corporate profits still lend support — Nvidia at $4.5 trillion and OpenAI at $500 billion show peak enthusiasm, yet fundamentals remain stronger than the dot-com era.
- Macro tailwinds and sector breadth are driving momentum: AI capex is boosting GDP, while small caps, utilities, and REITs join the rally on expectations of Fed rate cuts.
- Bubble risk is rising as sentiment overheats; the next phase may see rotation into under-owned markets or infrastructure plays as investors seek sustainable returns.
Backdrop: OpenAI’s AMD deal extends the capex cycle
Just when investors wondered if the AI euphoria had peaked, OpenAI signed a multi-year deal with AMD to secure up to 6 GW of GPU capacity, starting with about 1 GW in 2026. The agreement also gives OpenAI warrants to buy up to ~10% of AMD shares at a token price, tied to performance milestones.
It’s a strategic move to diversify beyond Nvidia, signalling that OpenAI expects to need massive compute for years. This follows other big moves in recent weeks:
- OpenAI–Nvidia partnership: expansion of its data-center deployments, reportedly involving up to 10 GW of Nvidia systems.
- OpenAI–Broadcom chip project: development of a custom AI accelerator targeted for 2026.
- Anthropic’s $13B funding round and new model launches, continuing a wave of capital inflows.
Together, these announcements show one message loud and clear: the AI capex boom is not slowing down, rather it is institutionalizing.
How did we get here
Nvidia leads the charge at $4.5 trillion in market cap, while OpenAI’s $500 billion valuation makes it the world’s most valuable private firm, surpassing SpaceX. With such stratospheric figures, investors are asking: how much bigger can this bubble get—and when does it burst?
But interestingly, Nvidia’s valuation multiple has fallen even as its share price and market cap soared. The stock trades at 32x forward earnings, down from 36x in late 2022. That’s not a sign of weakness — it reflects surging profitability catching up to share-price growth. Nvidia’s EPS has exploded faster than its stock price, compressing its multiple even as demand for GPUs remains insatiable.
Meanwhile, the rest of the AI cohort has seen steep valuation inflation since ChatGPT launched:
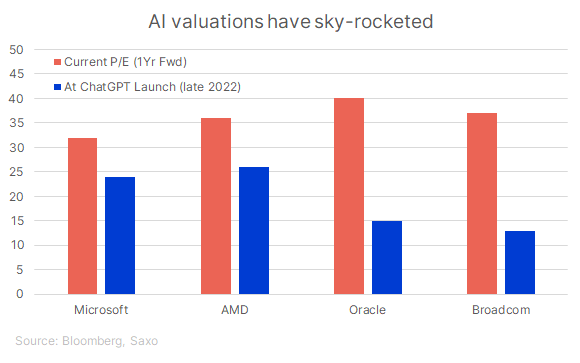
These valuations reflect investor conviction that AI will remain the defining growth engine of the decade — but they also leave little margin for disappointment.
Why bulls think “this time is different”
- Earnings strength: Unlike the early-2000s tech bubble, today’s AI leaders — Nvidia, Microsoft, Amazon, Meta, Alphabet — post genuine profits and robust cash flow. Their earnings are expanding fast enough to offset valuation inflation; Nvidia’s P/E has even compressed from 36x in 2022 to 32x as profits surged.
- Capex as a growth driver: Hyperscaler spending on AI data centers has lifted U.S. and global GDP, and capital commitments for 2026–27 suggest that momentum will remain strong.
- Emerging monetization: While infrastructure dominates headlines, AI services are already paying off in certain segments — cloud providers are monetizing AI workloads through premium pricing; enterprise software firms are upselling AI copilots; and chipmakers are seeing multi-year order visibility.
- Broader market participation: Beyond mega-caps, utilities, industrials, and REITs tied to AI infrastructure are gaining traction, a healthier setup than the 1999 rally.
- Policy tailwinds: Expected Fed rate cuts continue to support high-growth valuations.
- Relative sanity: Even with expansion, the Nasdaq 100’s 27x P/E still trails the 47x seen at the 2000 bubble peak.
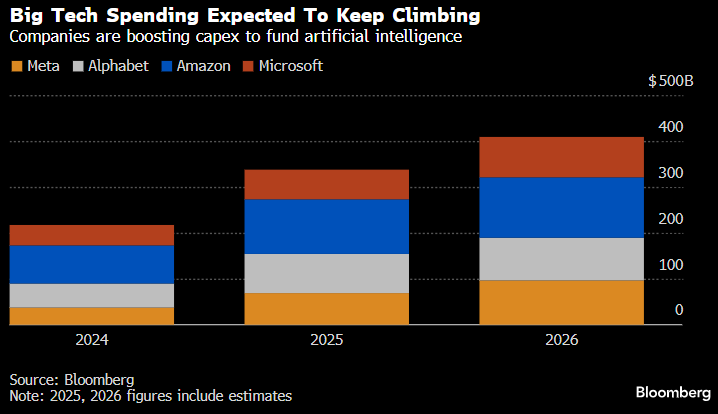
Why bears say it’s still a bubble
- Monetization gap: While capex keeps accelerating, revenue generation hasn’t caught up. The current wave of AI investment is infrastructure-led; tangible monetization through services and productivity gains may take longer. Bain & Co. estimates that by 2030, AI firms will need roughly $2 trillion in annual revenue to fund projected compute demand, yet could fall $800 billion short.
- Questionable productivity payoff: A study by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology found that 95% of organizations saw no measurable return on their AI investments. Researchers at Harvard and Stanford added that employees often produce “workslop” — AI-generated content that looks productive but fails to meaningfully advance tasks, potentially reducing productivity and wasting corporate resources.
- Execution headwinds: Even leading developers face diminishing returns from scaling models. Despite escalating compute budgets, new iterations such as GPT-5 have yielded incremental — not transformative — performance gains, calling into question the cost-to-benefit ratio of chasing artificial general intelligence.
- Capital misallocation risks: A wave of smaller and less proven firms is piling into the AI data-center buildout. Companies like Nebius and Nscale, both shifting from crypto mining to AI infrastructure, highlight how speculative capital often migrates to the next hot sector late in the cycle.
- Risk/reward imbalance: Many AI-linked stocks are now priced for near-flawless execution. With valuation multiples stretched and expectations sky-high, the margin for error has narrowed sharply.
- Energy and infrastructure bottlenecks: The AI build-out also depends on power availability. As electricity demand surges, data-center projects could be delayed by grid constraints and rising energy costs, limiting returns.
- Spillover risk: A pullback in AI leaders could weigh on broader equity indices, especially those heavily concentrated in tech. However, capital rotation into other regions and asset classes, including Europe, Japan, emerging-market debt, and precious metals, could limit systemic downside.
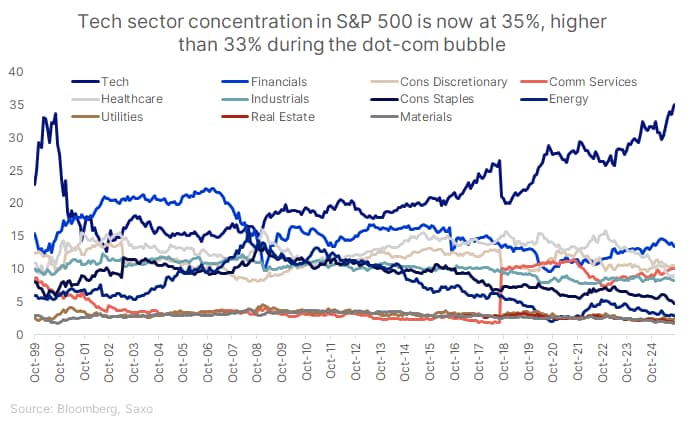
In summary, the bulls see a durable productivity revolution, where early profits and capex visibility justify high valuations.
On the other hand, the bears warn that the economic returns lag the hype and that infrastructure growth could outpace monetization.
Reality perhaps sits in the middle: AI is transforming balance sheets, but the payoff timeline may be longer and bumpier than markets are currently pricing.
What it means for investors
1. Stay core, but broaden exposure
AI remains a multi-year structural theme, but leadership will evolve. Investors can stay positioned in core enablers — Nvidia, Microsoft, AMD, Broadcom — while gradually adding second-order beneficiaries such as semiconductor equipment makers, data-center REITs, utilities, and power-grid players. The next leg of returns could come less from model creators and more from those powering and maintaining the AI infrastructure.
Explore Saxo’s AI Value Chain Theme Basket for diversified exposure across the ecosystem of hardware, software, and infrastructure enablers.
2. Focus on profit conversion
The market is shifting from “build” to “monetize.” Investors should favour firms demonstrating clear revenue pathways, such as AI-driven subscription upgrades, enterprise productivity tools, or cloud workload pricing tied to AI usage. Watch for gross-margin improvement and pricing power, not just headline model launches. Prioritize companies with strong balance sheets, recurring revenues, and disciplined capex over speculative entrants chasing hype.
3. Diversify geographically
While U.S. tech remains dominant, AI monetization and valuations in Asia — especially China — are lagging, creating potential catch-up opportunities. Chinese firms are advancing in AI infrastructure, model deployment, and industrial applications at lower multiples.
Explore Saxo’s China AI Shortlist to identify key plays across semiconductors, cloud, and automation that may benefit as global AI demand broadens.
4. Hedge the hype
Given stretched valuations, short-term volatility is inevitable. Use periods of exuberance to trim exposure to the most crowded names and add on dips in quality compounders. Balanced portfolios can also include gold, energy, or defensive sectors that may benefit if sentiment cools.
Balanced portfolios can also include:
- Gold and silver miners for diversification and inflation hedging — see Saxo’s Miners Shortlist
- Emerging market stocks as rotation opportunities — see the Emerging Markets Shortlist
- Dividend stocks and ETFs for steady income — browse the Dividend Shortlist
Risks to the view
- Execution delays: OpenAI’s AMD rollout begins only in 2026. Any delays in chip supply, HBM memory, or data-center construction could push out revenue recognition and hurt sentiment.
- Profit compression: As multiple GPU vendors enter the field, pricing power may erode, particularly if AMD, Broadcom, and custom chips succeed. This could compress margins for Nvidia and peers.
- Demand moderation: If AI adoption plateaus — for instance, if enterprises delay deploying AI tools due to costs or regulation — earnings expectations may outpace real-world monetization.
- Overbuilt infrastructure: Over-investment in data centers could mirror the 2000s telecom build-out — real assets, but underutilized capacity if usage growth lags expectations.
- Competition and price pressure: An influx of low-cost Chinese AI models could intensify price wars and compress margins for U.S. peers.
- Monetary tightening or inflation flare-ups: A reversal in Fed policy or higher long-term yields could pressure high-multiple tech stocks, leading to valuation derating.
- Geopolitical and regulatory headwinds: Export restrictions on advanced chips to China, data-sovereignty rules, or rising electricity costs could distort supply chains and raise costs.
Bottom line
AI remains a cornerstone of the next growth cycle, but investors should move from concentration to conviction. The smart approach is to stay invested in structural leaders, diversify by geography, and focus on companies that can monetize AI profitably rather than simply spending on it.
The instrument(s) referenced in this content may be issued by a partner, from whom Saxo receives promotional fees, payment or retrocessions. While Saxo may receive compensation from these partnerships, all content is created with the aim of providing clients with valuable information and options..
